Role Of Powder Morphology On Α-Phase Content In Plasma Sprayed Alumina Coatings
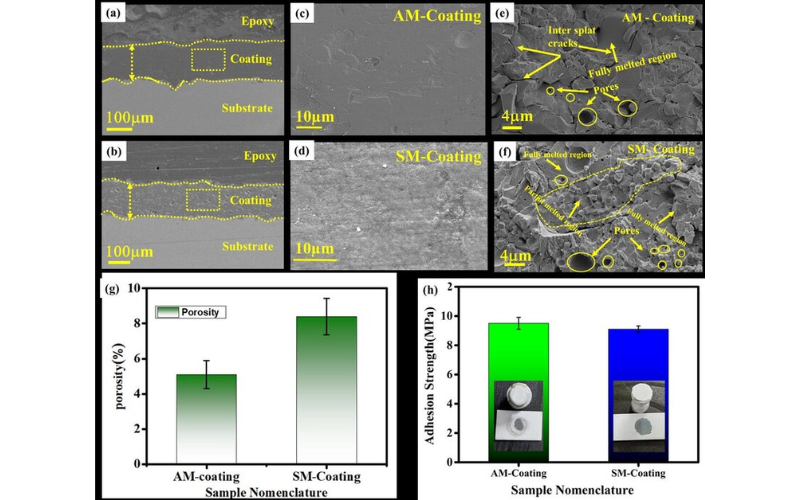
Despite various studies addressing the retention of α phase in thermal sprayed alumina coatings, a noticeable research gap persists regarding the impact of feedstock morphology on phase retention and properties. In this work, we explored this simple way to enhance the retention of the α phase and studied its impact on mechanical and dielectric properties. To achieve this, we deposited alumina powders with two different morphologies (such as angular and spherical) with similar particle size using plasma spraying. After deposition, we quantified the retention of α phase present in the coatings using the Rietveld refinement method. From this analysis, we noticed that spherical morphology (SM) powder exhibited the highest percentage of α phase retention (82.81 %) as compared to angular morphology (AM) powder (48.8 %). In turn, SM-coating demonstrated superior mechanical properties, with improvements in hardness, elastic modulus and fracture toughness of 21.9 % 13.7 % and 25 % respectively, compared to AM-coating. This improved mechanical properties in SM-coating is attributed to high α phase retention, synergistic effect of both fully melted (FM) and partial melted (PM) regions of coating microstructure which hindered the crack propagation. Furthermore, the SM-coating exhibited superior dielectric properties, with a dielectric strength 9.9 % higher than the AM-coating. This dielectric performance is ascribed to high retained α phase and generation of discontinuous crack due to presence of PM regions in the SM-coating. These findings suggest the impact of feedstock powder morphology on coating performance and offer avenues for optimizing coating processes in diverse technological fields.
Originally published at Ceramics International (Volume 50, Issue 14, 15 July 2024, Pages 25484-25493)
By Chintham Satish, K. Vijay Kumar, P. Sai Kiran, Santosh Kumar, Satish Indupuri, Rahul Kumar, Anup Kumar Keshri