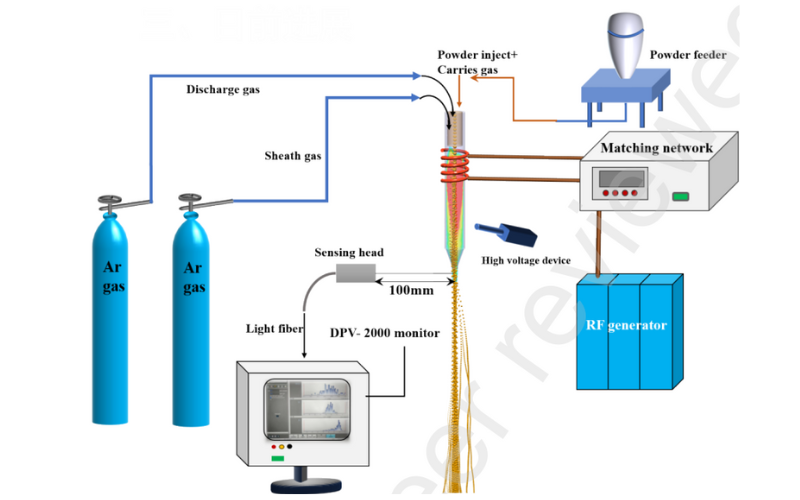
考虑热阻影响的射频热等离子体氧化铈粉末飞行加热过程研究
粉末颗粒在射频(RF)热等离子体中的飞行加热过程对等离子喷涂和球化具有重要意义。本研究通过实验和数值研究了二氧化铈(CeO2)粉末的这种加热过程。在实验中,将商用 CeO2 粉末(平均 30 μm)注入 RF 氩等离子体并用 DPV-2000 监测器测量温度。集成电磁、热流和传热预测的模型在氩等离子体中对粉末进行飞行加热。分别分析了不同直径的 CeO2 粉末的熔化过程、热阻效应下粉末的熔化时间。发现粉末颗粒的加热过程有三个主要阶段,其中加热阶段与无量纲参数 Biot 数有关。当 Biot≥0.1 时,热阻显著,尤其是对于较大的粉末。出口处颗粒的预测温度(1800-2880K)与实验测量结果一致。
关键词:射频热等离子体、热阻效应、加热过程、比奥数
最初发表为 SSRN 论文(发布时间:2024 年 8 月 26 日)
作者:Yi Su、Ruizhe Liu、Hilal Ahmad、Peng Zhao、Xingyue Jin、Hailong Zhu