添加 H2 对使用等离子炬从锆石 (Zrsio4) 制备 Zro2 粉末的影响
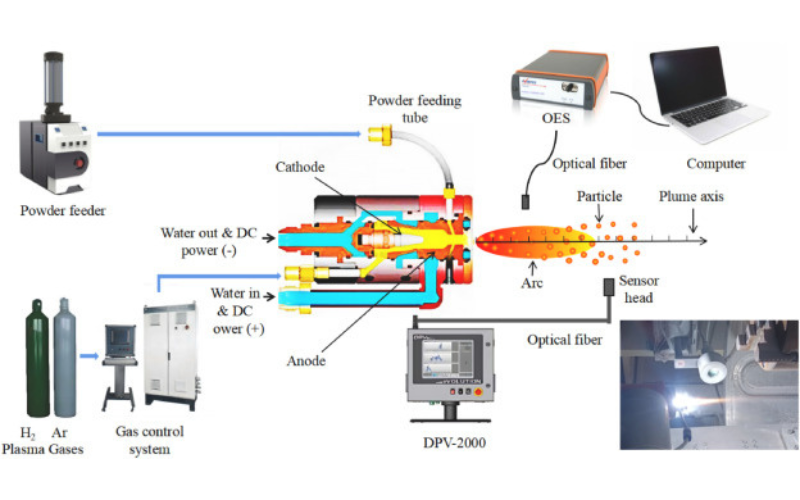
本研究利用等离子炬从锆石(ZrSiO4)制备高纯ZrO2。在放电气体Ar中加入H2,改善了等离子体的物理参数,并起到还原剂的作用,促使ZrSiO4热解反应不可逆。ZrSiO4粉末通过送粉装置内部送入直流电弧等离子炬,直流炬产生的热等离子体可以在短时间内充分加热所有的ZrSiO4,从而进行热解、提取和分离,最终得到高纯度的ZrO2。结果表明,在工作气体中加入H2,通过提高等离子体温度,提高了火焰中物料的温度,从而促进了ZrSiO4的热解。物料的温度为2500~2600℃,高于热解产物SiO2的沸点,同时保持了ZrSiO4和ZrO2的高熔点。此外,H2等离子体在热解反应中充当还原剂,与产物中的O结合,阻止ZrSiO4热解反应的可逆性,仅保留ZrO2。
最初发表于《Ceramics International》(第50卷,第1期,B部分,2024年1月1日,第1360-1369页)
作者:Chuanwen Geng、Peng Zhao、Muquan Wu、PeiGuang Yan、Xiang Gao、Jiangang Li、Jianjun Huang、Xiaodong Lin、Yiman Jiang、Xingyue Jin、Meihua Zeng